In the complex world of audio equipment, terms like speaker efficiency, sensitivity, and power often crop up. These concepts can seem daunting at first, especially when choosing the best speaker to meet your audio needs.
Efficiency is often used to describe speakers, but what does it mean?
Speaker efficiency refers to how effectively a speaker converts power into sound. It is expressed as a percentage and is a ratio of electrical input power to acoustic output power. It generally varies between 0.2% and 2%.
Efficiency and sensitivity often get used interchangeably, even by seasoned experts in the field. I use them interchangeably, but in theory, they are not the same thing.
Although speaker efficiency and sensitivity are not the same, they tell us the same thing. It is possible to convert speaker sensitivity to efficiency and vice versa.
Higher-efficiency speakers require less power to achieve the same volume, making them more efficient and suitable for low-powered amplifiers.
In this article, I will attempt to explain speaker efficiency. I will do my best to show how it is not the same as sensitivity, shedding light on the subtle differences between sensitivity and efficiency and helping guide you to understand what speaker efficiency really means.

What Does Speaker Efficiency Mean?
Speaker efficiency tells us how well a speaker can convert electrical energy (power) into acoustic energy (sound).
When a certain amount of electrical power is fed into a speaker, the speaker will produce a corresponding sound volume. The speaker’s efficiency measures how loud the sound will be for a given input power.
It’s important to note that this doesn’t necessarily relate to the quality of the sound but rather its volume.
High-efficiency speakers can produce a louder sound with less power, making them great for setups with lower-power amplifiers. Conversely, a low-efficiency speaker might require more power to reach the same volume level.
What Is The Difference Between Sensitivity And Efficiency?
Both sensitivity and efficiency relate to a speaker’s output, and they tell you the same thing.
From a theoretical definition standpoint, sensitivity refers to the loudness that a speaker can deliver per watt of power at a one-meter distance and is measured in decibels (dB).
Efficiency can be defined as a measure of how effectively a speaker converts power (electrical energy) into sound (acoustic energy), expressed as a percentage.
When you examine both of these concepts, they are telling us the same thing, i.e. how much power went into the speaker and how much acoustical power came out.
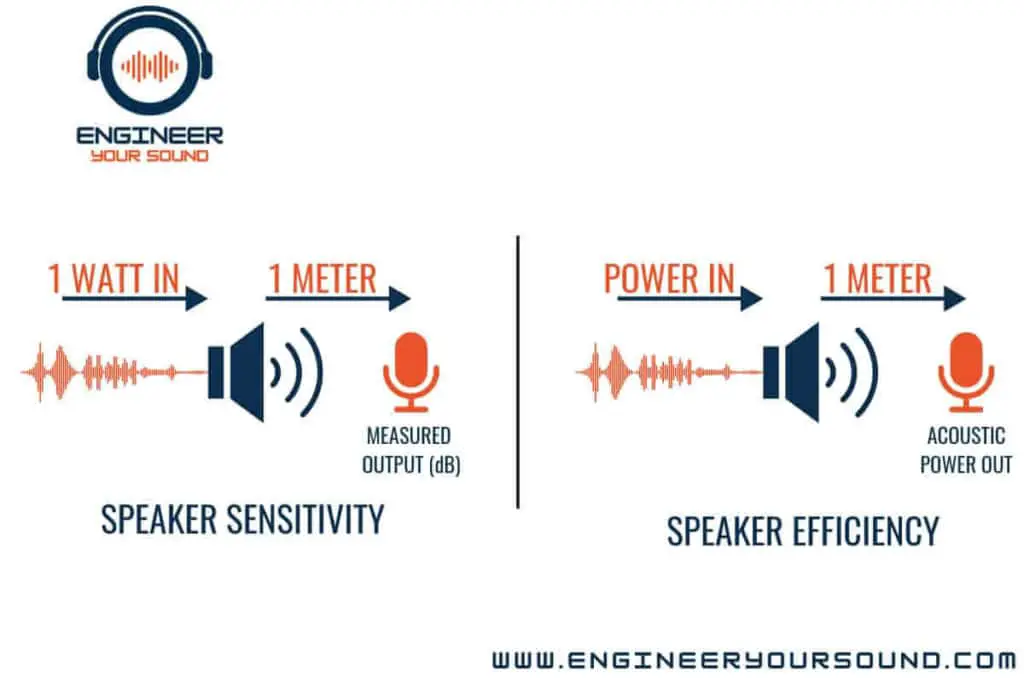
A speaker can be highly sensitive (i.e., capable of producing loud sound with little power) but not necessarily efficient in terms of converting most of the input energy into sound.
Conversely, a speaker could be efficient at energy conversion but not particularly sensitive, meaning it would need more power to achieve the same volume as a more sensitive speaker.
In essence, sensitivity is about loudness per watt, while efficiency is about energy conversion.
Do Speaker Manufacturers Publish Speaker Efficiency Values?
Not all speaker manufacturers publish speaker efficiency values. Some brands may focus more on sharing sensitivity ratings, as these are easier to measure and are often higher, making for more compelling marketing. However, a few manufacturers do include efficiency ratings in their specifications, allowing consumers to make more informed decisions.
If efficiency ratings are not directly provided, they can be calculated using the speaker’s impedance, power handling, and sensitivity ratings.
If you know a speaker’s sensitivity value, you can use the following formula to convert sensitivity to efficiency.
Efficiency = 10^(sensitivity-112)/10To then convert the efficiency value to a percentage, simply multiply your result by 100
For example, let’s assume you have a speaker with a sensitivity of 97 dB. To find the efficiency of this speaker, you slot this value into the formula.
Efficiency = 10^(97-112)/10 = 0.031
Converting our answer to a percentage, a speaker with a sensitivity of 97dB has an efficiency of 3.1%.
If you struggle with doing your own calculations, this calculator can help.
Who Uses Speaker Efficiency Values?
Speaker efficiency values are particularly useful for sound engineers, audiophiles, and anyone needing to optimize their audio setup.
Sound engineers use these values to ensure that the amplifiers and speakers they select will provide the desired audio output for a given venue.
For audiophiles, understanding speaker efficiency can help achieve the best possible sound quality for their home stereo system.
Consumers, in general, can use efficiency ratings to make more informed decisions when buying speakers and to better understand how much power their speakers will demand from their amplifiers.
From my experience, speaker sensitivity is the figure that most consumers want to know, and if you look on the websites of the world’s largest speaker manufacturers, you will most likely find the speaker sensitivity value published, which you can use to convert to efficiency if needed.
Do High-Efficiency Speakers Sound Better?
High-efficiency speakers do not inherently sound better than their lower-efficiency counterparts.
While a high-efficiency speaker can produce a louder sound with less power, the sound quality is influenced by numerous other factors, such as the speaker’s design, materials used, construction quality, and even the acoustics of the room where it is used.
A well-designed, low-efficiency speaker can deliver superior sound quality compared to a poorly made, high-efficiency speaker. Thus, while efficiency is an important consideration, particularly in terms of power requirements and volume, it should not be the sole factor when assessing a speaker’s sound quality.
It is crucial to also consider other specification aspects and user reviews to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the speaker’s performance.
How Many Watts is a Good Speaker?
When you first get started with speakers, understanding the concept of wattage and impedance can be tricky. I have often been asked, “How many watts is a good speaker?” and if “8ohm or 16ohm speakers are better.
There isn’t a one-size-fits-all answer to how many watts a good speaker should have, as this largely depends on the size of the listening room, the type of music you listen to, and how loud you like your music to be.
In a smaller room, a speaker with a power rating of 10 to 20 watts could be enough. For larger rooms or for people who enjoy louder music, a speaker of 50 to 100 watts may be more suitable. For extremely large spaces or outdoor settings, you may even require speakers with power ratings in the hundreds of watts.
However, it’s essential to remember that wattage is not the sole determiner of sound quality. Other factors, such as the speaker’s design, materials used, and the efficiency rating, also play crucial roles.
Therefore, while deciding on the wattage, one must also consider these other factors to ensure superior sound output and satisfactory performance.
Is A 40W Speaker Loud?
For some, knowing how loud certain wattage speakers are can be useful to give an indication of what to expect.
The loudness of a 40W speaker largely depends on the speaker’s sensitivity, the size of the room, and the listener’s proximity to the speaker.
Generally, for small to medium-sized rooms, a 40W speaker can produce a sound level that is loud and dynamic enough for most listeners. However, if you’re in a larger room or open space, or if you prefer listening to music at high volume levels, a 40W speaker might not reach your desired loudness.
It’s also important to note that loudness isn’t everything. The overall sound quality, clarity, and richness of a speaker matter greatly for a pleasant listening experience.
Therefore, while a 40W speaker can be loud in certain scenarios, it’s essential to consider other factors, such as the speaker’s design, materials, and efficiency, when making your selection.
Final Thoughts
It is important to be aware of speaker efficiency for optimizing audio setups, be it for professional sound engineers, audiophiles, or everyday consumers.
While it is tempting to focus solely on power ratings or loudness when selecting a speaker, these factors are just a part of the larger picture.
A speaker’s design, the materials used in its construction, and the acoustic characteristics of the environment all play crucial roles in determining sound quality.
Therefore, it is essential to consider these factors holistically while making a choice. Remember, a well-informed decision goes a long way in enhancing your auditory experience.
